

P2P Crypto Trading in Africa — The Unstoppable $100B Market
Africa’s crypto landscape is buzzing with energy—and nowhere is that more evident than in the peer-to-peer (P2P) trading market. Despite government crackdowns and regulatory hurdles, countries like Nigeria, Kenya, and Ghana are not just surviving; they’re thriving. With an estimated market value of over $100 billion, Africa’s P2P crypto trading scene is transforming how people access financial services, transfer money, and even build wealth. Let’s dive into this unstoppable market, explore the factors behind its explosive growth, and see how local trends and innovations are adding that unique African spice to the global crypto story.
Introduction
Overview of P2P Crypto Trading in Africa
P2P crypto trading allows individuals to exchange digital currencies directly with one another without relying on a centralized exchange. Think of it as a digital barter system—just like traders in a busy African market haggling over prices—but in this case, they’re trading Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies.
The Growing Relevance of P2P in Africa’s Financial Ecosystem
In many African countries, traditional banking systems are either inaccessible or too expensive. P2P platforms fill that gap by offering a decentralized, cost-effective alternative that empowers people to transact with ease. With millions of unbanked citizens and a burgeoning mobile-first population, P2P crypto trading has become a vital tool for financial inclusion.
Why Africa’s P2P Market Is Unique
Economic and Social Context
Africa’s economic landscape is defined by its rapid urbanization, youthful population, and sometimes unstable local currencies. In Nigeria alone, inflation rates can soar above 20% per annum, pushing many to seek alternatives to their depreciating local currency. For instance, a Nigerian trader might see crypto as a way to preserve wealth or send money back home more efficiently.
Government Crackdowns and Regulatory Landscape

While some governments have imposed strict policies to curb crypto activity, these measures have often led to a surge in underground and P2P trading. The infamous Nigeria–Binance saga is a prime example—when official channels were restricted, traders simply moved to P2P platforms, fueling a remarkable growth in daily trading volumes.
Crypto as a Financial Lifeline
In regions where remittance fees can exceed 10% of the transferred amount, crypto offers an affordable and speedy alternative. Imagine sending money from a bustling market in Accra or Nairobi with a fraction of the cost and in minutes rather than days. That’s the promise of P2P crypto trading in Africa.
The $100B Milestone: Understanding the Size and Growth of Africa’s P2P Crypto Market
Over the past few years, Africa’s peer-to-peer (P2P) crypto trading market has not only captured global attention—it has exploded to reach a staggering $100 billion in trading volume. This milestone is the result of a perfect storm of factors uniquely present in Africa’s economic and social environment.
How the $100 Billion Milestone Was Achieved
Africa’s journey to the $100 billion mark is driven by several key elements:
- Rapid Mobile Penetration:
With mobile phone ownership soaring—over 50% in many regions and nearly ubiquitous in urban centers—the continent has witnessed an unprecedented adoption of mobile financial services. This digital leap has enabled millions to access and trade crypto directly from their smartphones, bypassing the need for traditional banking. - A Young, Tech-Savvy Population:
Africa boasts one of the youngest populations in the world. This demographic is not only quick to embrace new technologies but also eager to explore innovative financial solutions. Their comfort with digital transactions and social media has been a significant catalyst for the growth of P2P trading platforms. - The Urgent Need to Bypass Traditional Financial Constraints:
Many African economies face challenges such as high inflation, volatile local currencies, and limited access to conventional banking. In countries like Nigeria, where inflation can exceed 20% annually, crypto provides an alternative store of value and a means of transferring money more efficiently. This urgency to find reliable financial tools has driven widespread adoption of crypto, particularly on P2P platforms that offer lower fees and faster transactions.
P2P Trading Volumes by Country
The growth of Africa’s crypto market is not uniform across the continent; certain countries have emerged as true powerhouses:
Nigeria

Often cited as the continent’s crypto powerhouse, Nigeria is estimated to contribute over 40% of Africa’s P2P trading volumes. With a population of around 200 million and an economy where traditional banking is often out of reach for many, Nigerians have embraced crypto as both an investment and a means to secure their finances. Despite intermittent regulatory challenges, Nigerian traders remain resilient, constantly adapting to the dynamic crypto landscape.
Kenya:

Kenya’s reputation as a leader in mobile money, largely due to the success of platforms like M-Pesa, has translated seamlessly into the crypto space. In the past year alone, Kenya has seen P2P trading volumes soar by as much as 150%. The familiarity with digital wallets and cashless transactions has made it easier for Kenyans to transition from mobile money to digital currencies, cementing Kenya’s status as a major crypto hub.
Ghana:

Known for its vibrant entrepreneurial spirit, Ghana is rapidly emerging as a significant player in Africa’s crypto market. Contributing around 10–15% of the continent’s total P2P volumes, Ghana’s growth is driven by a combination of increasing crypto awareness among the youth and a robust informal financial network that values innovation. Ghana’s market, though smaller in absolute numbers compared to Nigeria or Kenya, is characterized by steady growth and a high level of user engagement.
Africa’s Place in the Global P2P Market
Africa represents only about 4–5% of the global population, yet its P2P crypto trading volume is disproportionately high. This remarkable performance positions Africa as a leader in decentralized finance on the global stage. Some notable points include:
- High Remittance Flows:
Africa is one of the largest recipients of remittances globally—with billions of dollars sent home by diaspora communities each year. P2P crypto trading platforms offer a cheaper and faster alternative to traditional remittance channels, cutting out intermediaries and reducing transaction fees dramatically. - Comparative Trading Volumes:
While regions such as North America and Europe have mature financial systems, Africa’s P2P market has grown rapidly due to necessity and innovation. In many cases, the daily trading volumes on leading African P2P platforms rival those in more developed markets, underscoring the continent’s vital role in the global crypto ecosystem. - Global Impact on Decentralized Finance:
Africa’s adoption of P2P trading is influencing global trends. The resilience and innovative spirit seen on the continent are setting new standards for how decentralized finance can work in environments with limited access to traditional financial services. This not only boosts Africa’s stature but also provides a blueprint for emerging markets around the world.
The achievement of a $100 billion P2P trading volume in Africa is a testament to the continent’s innovative spirit, resilience, and the critical role that crypto plays in its financial ecosystem. Rapid mobile adoption, a youthful and tech-savvy population, and the pressing need to bypass traditional financial barriers have all contributed to this milestone. As Africa continues to lead by example, its P2P market is not only thriving locally but also influencing the global decentralized finance landscape.
Factors Driving Growth in P2P Trading
Inflation and Currency Devaluation:
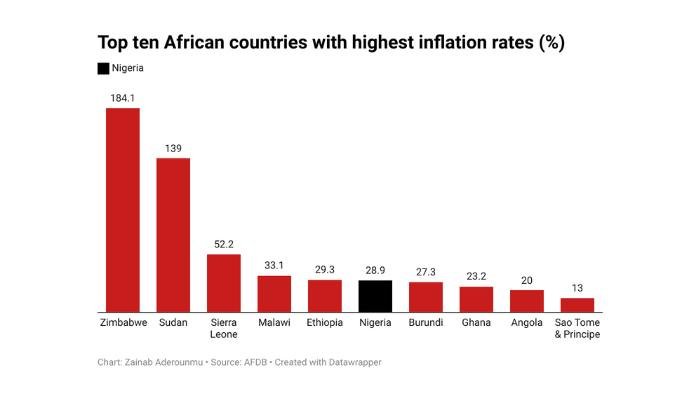
In many African countries, hyperinflation and currency devaluation force people to look for alternative stores of value. Cryptocurrencies offer a hedge against these economic instabilities, making P2P trading a lifeline for preserving wealth.
Lack of Access to Traditional Financial Services:
With up to 60% of Africa’s adult population unbanked, traditional financial services remain out of reach for many. P2P platforms allow individuals to transact, invest, and save without ever needing a bank account.
Mobile Money Integration and Rising Smartphone Penetration:
Africa is home to some of the world’s highest mobile money adoption rates. With smartphone penetration rising to over 50% in many countries, digital platforms are rapidly becoming the default way to manage money, fueling P2P crypto adoption.
Ease of Remittance:
Remittances play a critical role in African economies, with billions of dollars sent home by diaspora communities each year. P2P crypto trading offers a cheaper and faster alternative to traditional remittance services, cutting fees and processing times dramatically.
Country Spotlights: The Big Players in P2P Trading
Africa’s P2P crypto trading landscape is as diverse as it is dynamic. Three countries in particular—Nigeria, Kenya, and Ghana—stand out as trailblazers driving innovation and adoption across the continent. Let’s take a closer look at these market leaders, explore what makes them unique, and delve into some of their inspiring success stories.
Nigeria: Africa’s P2P Powerhouse
Why Nigeria Leads in P2P Trading
Nigeria is widely recognized as the continent’s crypto powerhouse. With a population exceeding 200 million—more than half of which are under 30—the country has a vibrant, youthful demographic hungry for financial empowerment and innovation. Over 100 million Nigerians are estimated to engage in digital transactions daily. High mobile penetration (with smartphone usage in major cities like Lagos and Abuja often surpassing 80%) and the urgent need to hedge against persistent inflation (sometimes topping 20% annually) have pushed many Nigerians towards crypto as an alternative store of value and a more efficient remittance channel.
The Binance Saga in Nigeria

Nigeria’s journey hasn’t been without its bumps. In February 2021, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) halted banks from facilitating crypto transactions—a move that led to a de facto ban on crypto. At the time, then-governor Godwin Emefiele famously dismissed cryptocurrencies as “money out of thin air.” Fast forward to December 2023, when the new CBN Governor, Olayemi Cardoso, overturned the ban, offering a glimmer of hope for crypto enthusiasts. However, the story took a dramatic turn when, within just two months, tensions escalated again—this time centering on Binance.
A brief timeline of the Binance saga in Nigeria:
- February 20, 2024: Binance suspended its P2P trading services amid growing regulatory scrutiny.
- February 21, 2024: The Binance website was blocked in Nigeria, cutting off access to millions of users.
- February 28, 2024: Nigerian authorities detained two key Binance employees—Tigran Gambaryan, former Crypto-Focused US Federal Agent leading Binance’s Criminal Investigation team, and Nadeem Anjarwalla, Binance’s Regional Manager for Africa—after a meeting with the EFCC and the Office of the National Security Adviser (ONSA).
As a result, Binance no longer offers any naira services in Nigeria, forcing traders to look for alternatives. Despite these setbacks, Nigeria’s P2P market has bounced back robustly, with traders quickly shifting to other platforms, ensuring that the momentum in the Nigerian crypto ecosystem remains unbroken.
Kenya: The Rise of a Tech-Driven Crypto Economy
Mobile Money’s Role in Kenya’s P2P Boom
Kenya is often celebrated for its groundbreaking mobile money revolution, led by the iconic M-Pesa. With over 40–50 million active users, M-Pesa has fundamentally redefined financial transactions in Kenya. This pre-existing familiarity with digital money paved the way for the swift adoption of crypto. In fact, Kenya’s P2P trading volumes have surged by up to 150% in the past year, as Kenyans leverage mobile-friendly platforms to trade cryptocurrencies with ease.
Government Policies and the Crypto Landscape
Kenya’s regulatory environment is more cautious compared to Nigeria, but it has not stifled innovation. Instead, regulators have pushed for decentralized solutions that operate alongside traditional banking systems. This has spurred local entrepreneurs to develop creative, tech-driven crypto tools and services. From crypto remittance apps to blockchain-based savings solutions, Kenya’s innovative ecosystem continues to thrive, making it a pivotal market for P2P trading on the continent.
Ghana: A Growing Hub for Crypto Enthusiasts
Youth-Led Adoption and Crypto Awareness
Ghana is quickly emerging as a vibrant center of crypto innovation, fueled largely by its young and dynamic population. In urban centers like Accra and Kumasi, university courses on blockchain technology, local crypto meetups, and vibrant social media discussions have driven a surge in crypto awareness. Ghana’s youth view crypto not only as a speculative asset but as a tool for economic empowerment and wealth creation.
Financial Barriers Driving P2P Growth
The traditional banking system in Ghana is often seen as expensive and inaccessible, particularly for the underbanked. This has led many citizens to turn to P2P crypto trading as an alternative, bypassing high fees and cumbersome bureaucratic processes. As a result, P2P platforms have become a community-driven way to build wealth and achieve financial inclusion, making Ghana one of the fastest-growing crypto markets in Africa.
Major Platforms Dominating P2P in Africa
4.1. Paxful

Paxful was a trusted name in P2P crypto trading Known for its user-friendly interface, extensive network, and robust security measures, Paxful has become a household name in Africa. With over 10 million registered users globally, the platform offers a wide range of local payment methods and supports numerous currencies, making it especially appealing to African traders.
Why Paxful Is Popular in Africa
The key to Paxful’s success in Africa lies in its deep understanding of local financial ecosystems. By prioritizing local payment options—from bank transfers to mobile money—it has effectively bridged the gap between traditional financial services and the digital economy, making crypto accessible even to those who have never interacted with a bank.
4.2. Binance P2P
How Binance Entered and Conquered the African P2P Space
Binance’s entry into Africa was marked by its robust P2P trading platform, which quickly garnered a large user base by offering competitive fees, a wide variety of payment options, and stringent security features. At one point, Binance P2P was the go-to platform for many African traders looking to convert fiat to crypto and vice versa.
The Binance Saga and Its Impact on the Market
However, as detailed in the Nigeria spotlight, Binance’s journey in Africa has been tumultuous. After the Nigerian government’s crackdown and subsequent ban on crypto-related transactions in February 2021, Binance found itself in hot water. Despite an apparent reversal of the ban in December 2023 by the new CBN Governor, issues resurfaced in early 2024—leading to a suspension of Binance’s P2P services, website blocks, and the detention of key Binance staff in Nigeria. These events have forced traders to pivot to other exchanges like Bybit, yet Binance’s initial impact and its innovative platform remain influential in shaping the market.
Competitive Edge and Volume Growth
Even with the challenges, Binance’s P2P platform demonstrated resilience. Its competitive fee structure and diverse payment options made it an attractive option, and its temporary suspension only spurred market participants to seek alternative platforms, further highlighting the inherent strength and adaptability of Africa’s P2P ecosystem
Decline of Legacy Platforms and Emergence of New Entrants
LocalBitcoins, once the pioneer in P2P crypto trading, has seen its prominence wane as newer, more technologically advanced platforms enter the market. These new entrants offer improved user interfaces, faster transaction times, and enhanced security features. They are capitalizing on the shortcomings of legacy systems, providing a more streamlined and reliable experience for African traders.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of P2P Trading in Africa
Africa’s P2P crypto trading ecosystem is evolving at breakneck speed. Several key trends are not only shaping the present but also setting the stage for a robust future. Here’s a deeper look into these trends:
Increased Adoption of Stablecoins
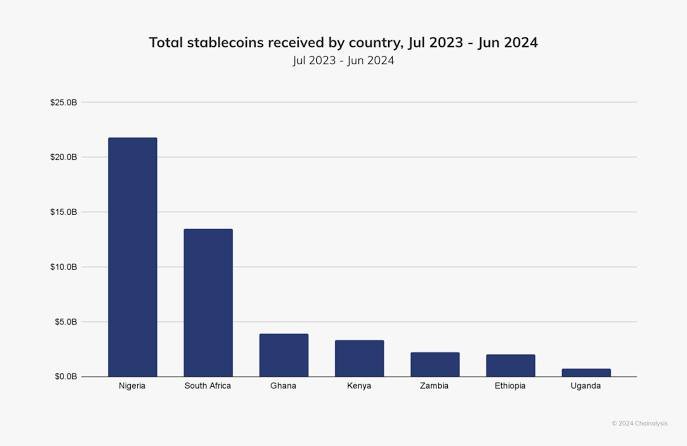
Stablecoins, such as USDT and cUSD, have become the backbone of P2P trading across Africa. Their primary appeal lies in their lower volatility compared to traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. In countries where local currencies can lose value rapidly—Nigeria’s naira, for instance, has seen devaluation rates exceeding 15% annually—stablecoins provide a much-needed refuge. They serve as a reliable store of value and enable traders to hedge against unpredictable currency fluctuations.
Consider this: In Nigeria and Kenya, where over 80% of urban dwellers own smartphones, many are turning to stablecoins for everyday transactions. With daily trading volumes on major P2P platforms often exceeding millions of dollars, stablecoins are helping users mitigate risks while still reaping the benefits of digital finance. For example, a Nigerian trader can convert local currency into USDT almost instantly and use it to purchase goods or transfer funds internationally with minimal fees—a critical advantage when traditional remittance services can charge as much as 10% per transaction.
Regulatory Shifts and Possible Legalization
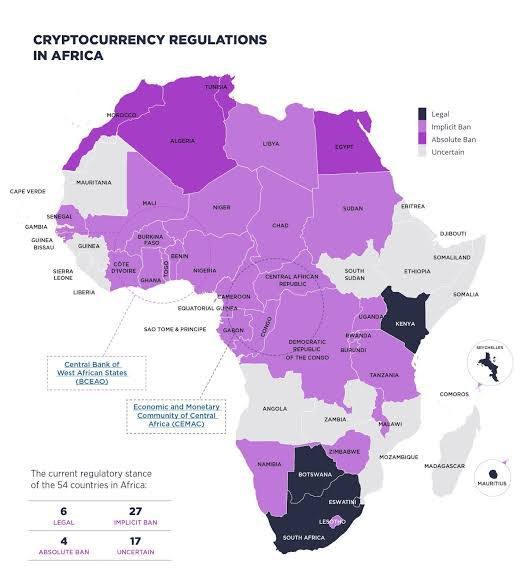
The regulatory landscape across Africa is in flux, with governments actively trying to balance innovation with risk control. In recent years, several African nations have started clarifying their policies toward cryptocurrencies. This shift is beginning to boost investor confidence, as clear regulations reduce uncertainty and foster a more stable trading environment.
For instance, countries like Kenya and Ghana have moved from a vague regulatory stance to more structured frameworks that protect investors while encouraging innovation. Although there are still instances of regulatory clampdowns—Nigeria’s dramatic Binance saga being a prime example—the overall trend suggests a slow but steady move toward legalization and more supportive policies. If these favorable regulations continue to take shape, we can expect even greater growth in P2P trading, as more investors will be willing to enter a market where the legal risks are minimized.
Integration of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Tools
The fusion of P2P trading with DeFi protocols is the next frontier in Africa’s crypto evolution. By integrating traditional P2P trading with lending, staking, and yield farming, users can not only trade but also generate passive income on their digital assets. This synergy is opening up entirely new revenue streams and creating a more holistic financial ecosystem.
For example, imagine a trader in Accra who not only uses P2P platforms to buy and sell crypto but also leverages DeFi tools to earn interest on stablecoins or participate in liquidity pools. Such integration can lead to significantly higher returns. Recent data from several African DeFi platforms indicates that users who diversify into staking and yield farming have seen annualized returns upwards of 20–30%, compared to the typical gains from spot trading alone. The blending of these systems makes the crypto market more versatile and accessible, especially for those who might be underserved by traditional financial institutions.
Risks and Challenges in the P2P Market
While the future of P2P trading in Africa is bright, the market is not without its challenges. Addressing these risks head-on is critical for ensuring sustainable growth.
Regulatory Risks and Clampdowns
Regulatory uncertainty remains a significant concern. Even as some African nations move toward clearer policies, sudden clampdowns can disrupt trading volumes and shake investor confidence. For instance, the Nigerian government’s intermittent bans and subsequent reversals have led to market instability, causing traders to shift platforms quickly. The volatility induced by regulatory actions can lead to temporary liquidity issues, which might scare off more risk-averse investors.
Fraud and Security Concerns
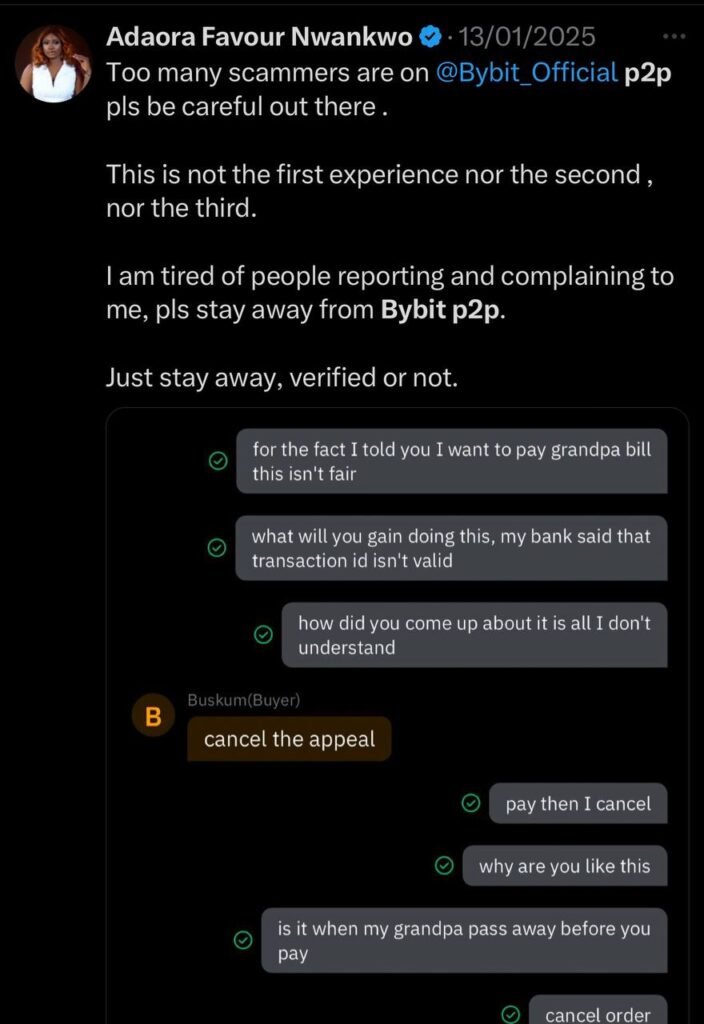
P2P platforms, by their very nature, are vulnerable to fraud and scams. With transactions often taking place without a central authority, there’s an increased risk of fraudulent schemes and security breaches. In markets where users are still learning about digital finance, a single high-profile scam can damage the trust necessary for widespread adoption. Robust security measures and user education are paramount to mitigating these risks. Many platforms are now implementing multi-factor authentication, escrow services, and identity verification protocols to build a safer trading environment.
Liquidity and Price Volatility Issues
While volatility creates opportunities for short-term gains, it also poses substantial risks. Sudden liquidity crunches or price swings can result in significant losses for traders who are not well-prepared. For example, during periods of market stress, some P2P platforms have experienced temporary drops in liquidity, making it harder for traders to exit positions at desired prices. This risk underscores the importance of robust risk management strategies and diversification across different assets and platforms.
The Road Ahead: What’s Next for P2P Trading in Africa?
Opportunities for Growth
The future for P2P trading in Africa is laden with opportunities. With millions of unbanked individuals and rapidly increasing mobile penetration, there is enormous potential to extend financial services to underserved communities. Financial inclusion initiatives spearheaded by both governmental and private sectors are already making headway in bridging the gap. In Nigeria, Kenya, and Ghana, efforts to expand digital infrastructure and enhance mobile connectivity are expected to further drive P2P trading volumes, unlocking new avenues for economic empowerment.
Future Projections and Market Potential
Looking forward, many analysts project that Africa will not only maintain its leadership in P2P crypto trading but could also serve as a model for other emerging markets. As technology continues to evolve and regulatory frameworks become more favorable, Africa’s P2P market could see exponential growth. Projections suggest that by 2027, Africa’s P2P trading volume could double, driven by both increased participation from the local population and a surge in institutional investments attracted by the market’s potential. This continued growth is expected to have a ripple effect, encouraging further innovation and driving deeper integration of digital financial services across the continent.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- P2P Trading Will Continue to Thrive: Africa’s unique economic and social conditions, coupled with its rapidly growing digital ecosystem, ensure that P2P crypto trading remains a formidable force.
- Local Innovation Drives Growth: Countries like Nigeria, Kenya, and Ghana are setting the pace with innovative solutions tailored to their unique challenges and opportunities.
- Stablecoins and DeFi Integration: The increasing adoption of stablecoins and the integration of P2P trading with DeFi protocols are unlocking new revenue streams and enhancing financial inclusion.
- Resilience Amid Regulatory Shifts: Even in the face of regulatory clampdowns—exemplified by the Binance saga in Nigeria—the market has demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptability.
A Look Beyond 2025
Africa’s P2P crypto market is not a fleeting trend—it represents a fundamental shift in how money is managed and transferred. Beyond 2025, the long-term impact of P2P trading is poised to reshape Africa’s financial landscape. As more citizens gain access to digital financial tools and regulatory frameworks stabilize, the continent could become a global leader in decentralized finance, driving widespread economic inclusion and digital innovation.







